Biomass as one possible answer to climate change.
What is biomass?
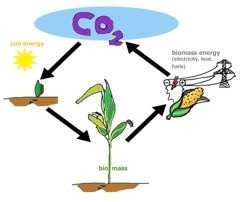
Biomass, a renewable energy source, is biological material from living, or recently living organisms, such as trees, crops, animals and plants, but also agricultural, urban and industrial wastes. Biomass is stored sun energy in the form of carbohydrates. All living things rely on that kind of energy.
Recently biomass has become one energy source to satisfy our growing energy need. Most of this biomass is used to gain electricity or heat while some of it is also used for the production of fibres or chemicals.
Why biomass?
Soon there will be 8 billion people living on our globe. This is an incredible number thinking that only one hundred years ago there were not even 2 billions! Mankind has grown tremendously and so has the need for energy. Until 150 years ago biomass gave people all the energy they needed – food as well as heat. Today we satisfy this need mainly by using fossil fuels like natural gas or petroleum. Burning fossil fuels produces CO2, a greenhouse gas. CO2 and other greenhouse gases act like a blanket around our planet: they let sun energy in but don’t let the heat out again. Using biomass instead of fossil fuels is one possible way of reducing the CO2 emissions on our planet.
Plants used for biomass energy take exactly the amount of CO2 out of the atmosphere that that is set free when they are burned or when they rot.
Raw materials used as biomass can be either crops that are especially grown for that purpose or agricultural, municipal or industrial organic wastes. Using wastes also helps reducing the amount of waste that ends up in landfills.
Environmental impact of biomass
+ Using biomass as a source of energy helps reduce the overall output of greenhouse gases. Today, we know that this is true for most fast growing crops (e.g. corn) and for organic wastes but not necessarily for forests.
+ Using biomass can help reducing the amount of organic wastes
-Using biomass as a fuel produces air pollution in the form of carbon monoxide, NOx(nitrogen oxides), particulates and other pollutants, in some cases at levels above those from traditional fuel sources such as coal or natural gas.
-Using biomass from forests often is not CO2 neutral for it takes a long time for the trees to grow again.
Questions for discussion
-Is it ethical to burn biomass when in other places people starve to death?
-Wouldn’t atomic energy be a possible way to avoid the production of CO2?
Biomass, a renewable energy source, is biological material from living, or recently living organisms, such as trees, crops, animals and plants, but also agricultural, urban and industrial wastes. Biomass is stored sun energy in the form of carbohydrates. All living things rely on that kind of energy.
Recently biomass has become one energy source to satisfy our growing energy need. Most of this biomass is used to gain electricity or heat while some of it is also used for the production of fibres or chemicals.
Why biomass?
Soon there will be 8 billion people living on our globe. This is an incredible number thinking that only one hundred years ago there were not even 2 billions! Mankind has grown tremendously and so has the need for energy. Until 150 years ago biomass gave people all the energy they needed – food as well as heat. Today we satisfy this need mainly by using fossil fuels like natural gas or petroleum. Burning fossil fuels produces CO2, a greenhouse gas. CO2 and other greenhouse gases act like a blanket around our planet: they let sun energy in but don’t let the heat out again. Using biomass instead of fossil fuels is one possible way of reducing the CO2 emissions on our planet.
Plants used for biomass energy take exactly the amount of CO2 out of the atmosphere that that is set free when they are burned or when they rot.
Raw materials used as biomass can be either crops that are especially grown for that purpose or agricultural, municipal or industrial organic wastes. Using wastes also helps reducing the amount of waste that ends up in landfills.
Environmental impact of biomass
+ Using biomass as a source of energy helps reduce the overall output of greenhouse gases. Today, we know that this is true for most fast growing crops (e.g. corn) and for organic wastes but not necessarily for forests.
+ Using biomass can help reducing the amount of organic wastes
-Using biomass as a fuel produces air pollution in the form of carbon monoxide, NOx(nitrogen oxides), particulates and other pollutants, in some cases at levels above those from traditional fuel sources such as coal or natural gas.
-Using biomass from forests often is not CO2 neutral for it takes a long time for the trees to grow again.
Questions for discussion
-Is it ethical to burn biomass when in other places people starve to death?
-Wouldn’t atomic energy be a possible way to avoid the production of CO2?
Biogas - an energy source of growing importance
Soon there will be 8 billion people living on our globe. This is an incredible number thinking that only one hundred years ago there were not even 2 billions!. Mankind has grown tremendously and so have some problems. By producing biogas we could fight two major problems of mankind.
Two problems of a growing mankind. The first is the growing amount of waste we produce – including also organic waste. When organic waste rots, it sets free CO2 and methane. Both gases are known to be greenhouse gases, which means, they make our earth warmer. And second, our modern society depends on the energy of fossil fuels such as oil, gas or coal. These fuels are limited and might be used up soon. Using them always means burning them, which again leads to a higher amount of CO2 in the atmosphere.
Biogas as a solution. Biogas is made of organic waste or agricultural crops especially grown for that purpose. Thus it reduces the amount of waste in our landfills. Biogas is also a powerful fuel, which can help to satisfy our energy needs in a sustainable and CO2 neutral way.
Production of biogas- If you produce biogas, you let biomass rot in the absence of oxygen. Under these “anearobic” conditions organic matter rots with the help of microorganisms to produce biogas. It is a mixture of methane CH4 (75-50%) and carbon dioxide CO2 (25-50%) and can be burned to carbon dioxide and thereby energy is produced.
Raw material for biogas production. Biogas can be made of almost any kind of organic material.
- organic wastes of cities, sewage sludge
- industrial waste water
- waste water of cities
- organic wastes of farming (straw, leaves , manure…)
Production of biogas from agricultural organic wastes. Biogas from organic farming wastes is usually produced in fermenters (also called digesters). Those are big containers in which the wastes are decomposed by bacteria in an atmosphere without oxygen. In Germany there are about 3000 such “mini plants”, in Austria there are about 120. Almost all of them use the biogas to produce heat and electricity. The biogas is used to run a motor that produces electricity in the first place and heat as a by-product.
Soon there will be 8 billion people living on our globe. This is an incredible number thinking that only one hundred years ago there were not even 2 billions!. Mankind has grown tremendously and so have some problems. By producing biogas we could fight two major problems of mankind.
Two problems of a growing mankind. The first is the growing amount of waste we produce – including also organic waste. When organic waste rots, it sets free CO2 and methane. Both gases are known to be greenhouse gases, which means, they make our earth warmer. And second, our modern society depends on the energy of fossil fuels such as oil, gas or coal. These fuels are limited and might be used up soon. Using them always means burning them, which again leads to a higher amount of CO2 in the atmosphere.
Biogas as a solution. Biogas is made of organic waste or agricultural crops especially grown for that purpose. Thus it reduces the amount of waste in our landfills. Biogas is also a powerful fuel, which can help to satisfy our energy needs in a sustainable and CO2 neutral way.
Production of biogas- If you produce biogas, you let biomass rot in the absence of oxygen. Under these “anearobic” conditions organic matter rots with the help of microorganisms to produce biogas. It is a mixture of methane CH4 (75-50%) and carbon dioxide CO2 (25-50%) and can be burned to carbon dioxide and thereby energy is produced.
Raw material for biogas production. Biogas can be made of almost any kind of organic material.
- organic wastes of cities, sewage sludge
- industrial waste water
- waste water of cities
- organic wastes of farming (straw, leaves , manure…)
Production of biogas from agricultural organic wastes. Biogas from organic farming wastes is usually produced in fermenters (also called digesters). Those are big containers in which the wastes are decomposed by bacteria in an atmosphere without oxygen. In Germany there are about 3000 such “mini plants”, in Austria there are about 120. Almost all of them use the biogas to produce heat and electricity. The biogas is used to run a motor that produces electricity in the first place and heat as a by-product.